NORTHERN NEVADA Public Health Serving Reno, Sparks & Washoe County
Frequently Asked Questions

FAQs
What are the Nevada Revised Statues and Nevada Administrative Codes relevant to Providers concerning communicable disease, including STDs/HIV? What do they say?
NAC 441A.230: Outlines the duty of health care providers in reporting a case or suspected case of communicable disease to health authorities. This Nevada Administrative Code enumerates requirements and content of the mandatory report by providers for communicable disease. Refer to box 5 for specific requirements.
NRS 441A.150: States that a provider of health care who knows of, or provides services to, a person who has or is suspected of having a communicable disease shall report that fact to the health authority in the in the manner prescribed by regulations of the Nevada State Board of Health. For STDs/HIV this is required within one day.
NRS 441A.165: States that health authorities shall, for the protection and welfare of the public, have access to all medical records, laboratory records and reports, books and papers relevant to the investigation which are in the possession of a provider of health care or medical facility being investigated or which are otherwise necessary to carry out the investigation. The determination of what information is necessary to carry out the investigation is at the discretion of the health authority.AIDS/HIV Prevention
Consequences of STDs
Some STDs are easily treated and some STDs stay with you for life. Other STDs are more of a nuisance than a health risk. Pubic lice, or 'crabs,' for example, itch a lot but don`t do any permanent damage. If you get an infection and you want to know how serious it could be, talk with your health care provider. There are four serious health consequences of some STDs:
- Blockage of the fallopian tubes which can lead to infertility and ectopic pregnancy
- Pregnancy loss and increased newborn deaths caused by transmission of the infection to the infant during pregnancy and childbirth
- Genital cancers for males and females
- Enhanced transmission of HIV/AIDS
Social and Psychological Consequences: The psychological impact of having a sexually transmitted disease can be difficult. Some persons become depressed or anxious. They fear recurrent outbreaks, transmission to sex partners, and difficulties in developing new relationships. Fortunately, proper treatment and knowledge about the true risks can greatly lessen all these effects.
Do condoms provide 100% protection from HIV?
Condoms are not 100% effective at preventing HIV transmission. When used correctly and consistently, condoms are highly effective and reliable in reducing the risk of transmitting HIV and most sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Condoms should be used EVERY TIME during sex when transmission of HIV (or other STDs) is possible. When condoms fail to work properly, it is most often because of improper and/or inconsistent use.
Condoms may not work as well against STDs spread through skin-to-skin touching, like herpes and genital warts, because condoms may not cover the infected areas.
Following these basic rules will reduce the already small chance of condom failure: - Experiment with different condoms and practice putting them on before intercourse. - Practice talking with your partner about your desire and intention to use condoms. - Use latex (rubber) or polyurethane (plastic) condoms. Avoid "natural skin" condoms, which have tiny holes, which may allow HIV and other STDs to be transmitted. - When using a male condom choose one that fits. Male condoms come in different sizes, shapes, and styles, but most condoms will fit most men. - Another choice is the Reality condom, which is made of polyurethane and is designed to fit inside the woman`s vagina for vaginal sex, and the anus for anal sex. Use the directions from the manufacturer that come with Reality condoms. - Open and handle condoms carefully. Never use a condom that is in a damaged package or is past its expiration date. Condoms should be stored loosely in a cool, dry place (not in your wallet or the glove compartment of your car) and kept where you can easily get them if you decide to have sex. - To reduce friction that can cause breakage, use plenty of water-based lubricant on the outside of the male latex condom and a small amount on the inside at the tip. With the Reality condom use plenty of lubricant on both the inside and outside. Some condoms come with lubricant, but often there is not enough, so additional lubricant is recommended. Never use oil-based lubricants like Vaseline, hand cream, Crisco, or mineral oil with latex condoms. Oil-based lubricants can rapidly break down latex and allow the virus to pass through. Water-based lubricants include K-Y Jelly, Slippery stuff, ForPlay, Astroglide, ID Lubricants and most contraceptive jellies. These can be found in grocery or drug stores next to the condoms. WARNING: Some lubricants contain nonoxynol 9, which can cause irritation. This irritation may increase the risk of HIV transmission. We do NOT advise the use of nonoxynol 9 or products containing it for STD and HIV prevention!The male condom should be put on after erection and before any sexual touch. Remember that pre-cum is also infected with HIV. The Reality condom should go in before sex - it can be inserted up to 8 hours before use. Never use the Reality and the male condoms together or two male condoms at the same time. - Some male condoms have a reservoir tip; some don`t. In either case, the tip of the condom should be squeezed while rolling it down onto the penis in order to leave an airless pocket to collect semen. If the penis is natural and has a foreskin, try pulling back the foreskin before unrolling the condom all the way down to the base of the penis. Some men don`t like to pull back the foreskin because they`ve found that the condom slides off when the foreskin is pulled back. If you have trouble with this, consider keeping the foreskin down before putting on the condom or try using a Reality condom with your partner. - After intercourse, withdraw the penis while still erect, holding the base of the condom to prevent it from slipping off or spilling semen. Remove the condom and wash the penis with soap and water. - Use a condom only once and dispose of it in the garbage; do not flush condoms down the toilet. Never reuse a condom. - Use a condom EVERY TIME during sex when transmission or acquisition of HIV is possible.
HIV is NOT transmitted by:
Casual Contact. HIV is a fragile virus outside the body. It quickly becomes inactive when exposed to air, soap and common disinfectants such as bleach.
There is no risk of getting HIV from: donating blood, mosquito bites, toilet seats, shaking hands, hugging, sharing eating utensils or drinking containers, food or objects handled by people with HIV or AIDS, spending time in the same house, business or public place with people who have HIV or AIDS.
How can HIV transmission from injection drug use be prevented?
The best way to avoid HIV infection (and other blood-borne infections like hepatitis B and C) from injection drug use is to stop injecting drugs. Drug treatment can help. If treatment is not available or you cannot quit on your own, use a brand new sterile syringe and needle every time you inject or divide drugs. Do not share drug using "works" with anyone else. This includes needles, syringes, cookers, cottons, mixing and bleaching water, and all other supplies. If you do not have new clean equipment, thoroughly disinfect all drug use tools with bleach before re-use. It is also important to dispose of used works safely. Discarding needles in the trash, on the street, or flushing them down the toilet is dangerous.
Drug use (including use of alcohol) can impair judgment and decision-making. This can increase risk for HIV, especially if you have sex while high. High or not, you can successfully use condoms and clean injection works. Plan ahead, carry condoms and stick to your prevention plan. *A person does not need a prescription to purchase syringes in Nevada. However, a pharmacist may refuse to sell to people based on their own judgment.
How can sexual transmission of HIV be prevented?
The only way to completely avoid the sexual transmission of HIV is to abstain from anal, oral and vaginal sexual. If you choose to have sex, it is safest when you practice monogamy with an uninfected partner. Monogamy is when two people have sex only with each other. For those with a new sex partner, both can abstain from sex, or use condoms every time during anal, vaginal and oral sex for at least 3 months and then get tested for HIV and other STDs. At that time, if both partners are HIV negative AND both partners are completely avoiding other risk behaviors (e.g., sharing needles or having other sex partners), then unprotected sex with each other is not a risk for HIV transmission. For someone with an HIV positive partner or a partner who does not know his/her HIV status or multiple sexual partners, touching, dry kissing, body rubbing, and mutual masturbation are the safest sexual activities. However, simple, skin-to-skin touching can spread other STDs. For any penetrative sex acts such as vaginal, anal or oral sex, condoms are highly effective at reducing the risk of HIV transmission when used consistently and correctly - every time, from beginning to end of each sex act. For more information on condom use see the answer to the question, "Do condoms provide 100% protection from HIV?"
How is HIV transmitted?
HIV can be transmitted when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or pre-cum), vaginal fluids, or breast milk from an infected person enters the body of an uninfected person. HIV must get into the bloodstream or body in order to cause infection. Transmission most often occurs during unprotected sex or during injection drug use when equipment is shared. An infected woman who becomes pregnant can transmit HIV to her baby during pregnancy or during birth, but this risk is significantly less if the woman takes antiretroviral drugs. She can also pass HIV to her newborn if she breastfeeds. Anyone infected with HIV can transmit it, whether or not they appear sick, have an AIDS diagnosis, or are successfully treating their infection with antiretroviral drugs. HIV is spread in the following ways: Unprotected anal, vaginal or oral sex HIV can enter the body during sex through the anus, vagina, opening at the end of the penis or mouth and through cuts, sores and abrasions on the skin. Unprotected anal and vaginal sex have the highest risk of infection. There are a growing number of reported cases where HIV has been transmitted during oral sex (mouth to genital contact), but oral sex is much less risky than anal or vaginal sex.
Anyone having unprotected sex (inserting or receiving partner) with an infected person is at risk of getting HIV. The person most at risk is the receiving partner. Heterosexually, women are at higher risk than men.
Blood exposure. Sharing needles or drug injection equipment can transmit HIV (and other viruses like hepatitis). After use, small amounts of blood can remain in the used needles, syringes, cookers, cottons, and water. This remaining blood can enter the body of the next user when any of these items are shared. If this blood is HIV infected, transmission can easily occur.
There is a very small but real risk of health care workers getting HIV from infected patients as a result of needle stick accidents or when blood gets into a worker`s open cut or a mucous membrane in their eyes, mouth or nose. The risk for health care workers is greatly reduced when universal precautions are carefully followed, such as safe disposal of sharps, wearing latex gloves, etc. Universal precautions also protect patients.
Very rarely in this country is HIV transmitted when receiving a blood transfusion, blood clotting factors, an organ or tissue transplant (the risk of acquiring HIV from a blood transfusion is approximately 1 in a million). Before 1985, there were no tests to screen blood and organ donations for HIV. Now, blood, organ and tissue banks extensively test all specimens for HIV and other blood-borne germs.
Mother to child If a woman is infected with HIV, she can give it to her baby during pregnancy, during birth, or by breastfeeding. Early in the epidemic, 25% (1 out of 4) of babies born to HIV-infected women in this country became infected with HIV. Now, in developed countries where early detection of HIV is possible, treatment with the latest antiretroviral medications can reduce this rate to about 1% (1 out of 100). All pregnant women should see a doctor, be tested for HIV, and if infected, obtain the best treatment.
Is there a cure for HIV and AIDS?
Not at this time. Medical providers have become much better at identifying, monitoring, and treating HIV infection and AIDS. In 1995, a new class of drugs known as protease inhibitors became available. These new medications, used in combination with other antiretroviral drugs, have dramatically improved the health and quality of life for many people living with HIV/AIDS. While there is not currently a cure or vaccine for HIV/AIDS, there are many things that people living with HIV/AIDS can do to remain healthy and to live longer. The first step for anyone who has HIV infection is to see a knowledgeable, experienced medical provider. This provider will be able to assess and monitor the infection, and, if appropriate, prescribe antiretroviral drugs. People at increased risk for HIV infection need to be tested for HIV antibodies every 3-6 months. This way they can seek medical care at the earliest possible opportunity if they become infected with HIV. Early detection can also reduce the chance of HIV transmission when people are most infectious. Although medical care and drugs are expensive, programs exist to ensure that people with HIV infection and AIDS can get the treatment and care they need.
What are STDs?
Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) are diseases that are spread through anal, oral or vaginal intercourse. Sharing drug injection equipment can also transmit some STDs such as HIV and Hepatitis B. Common STDs include: Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Hepatitis A Virus (HAV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), Hepatitis C Virus (HCV), Herpes Simplex Virus (Herpes), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Human Papilloma Virus (Genital Warts), Molluscum Contagiosum, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), Pubic Lice, Scabies, Syphilis, and Trichomoniasis.
What are the symptoms of a new HIV infection?
Between 50-90% of people with new HIV infections have mild to severe "flu-like" symptoms 2 weeks to 3 months from the time of HIV exposure. Others do not have any symptoms. In general, symptoms are not a reliable way to tell if someone has been infected with HIV; the only way to know for sure is to get tested. Many of the symptoms of early HIV infection are the same as for other, less serious illnesses. People who may have been exposed to HIV should see a doctor promptly if the following symptoms occur within 3 months of the exposure:
- A persistent fever of over 101 degrees that lasts more than 2 days without a known cause
- Constant tiredness
- Night sweats that soak your pajamas or sheets
- A persistent rash of unknown cause
- Persistent swollen glands (lumps under the skin) which occur in several places at once (especially the neck, armpits and groin)
- Sore throat
What is AIDS?
AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is a medical condition resulting from HIV infection, usually after many years. By the time a person is given an AIDS diagnosis by a doctor, HIV has seriously damaged the body`s immune system. There are effective treatments to prevent, as well as treat, these serious illnesses.
What is HIV?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is the virus that causes AIDS. HIV kills specific white blood cells (T cells), which are an important part of our immune systems. Without treatment, HIV gradually destroys the body`s defenses against disease (it takes an average of 8-10 years), leaving it vulnerable to many infections and cancers. But treatment with antiretroviral drugs can slow or stop the harmful effects of retroviruses like HIV, so that many people with HIV are living longer, healthier lives.
What is the HIV Antibody Test?
There are several types of HIV antibody tests used today. All are highly accurate at detecting HIV antibodies (HIV antibodies are specific proteins made in response to an HIV infection). After infection with HIV, however, it can take up to 3 months for enough HIV antibodies to develop to be detected by the test.
A negative HIV antibody test result means that a person does not have detectable HIV antibodies at the time of the test. Since it can take up to 3 months after HIV infection for enough antibodies to develop, a negative test result is reliable only if the person has not had any sexual or needle-sharing risk behavior (or other exposure to infectious body fluids) during the 3 months prior to testing. Some people with recent risk behavior will test HIV antibody negative, yet may have actually been infected during the previous 3 months. These people will be highly contagious and may easily transmit HIV to their sex and needle-sharing partners. A high proportion of HIV transmission may occur when people are unaware of their infection. Finally, a negative test result does not mean that a person is safe from future HIV infection. People who test HIV antibody negative are urged to continue to follow HIV prevention guidelines to avoid becoming infected. People who continue risk behaviors are advised to re-test at least every 6 months.
A positive HIV antibody test result means that HIV antibodies are present because the virus is present - the person is infected with HIV (with the exception of newborn babies who are born with their mothers` antibodies). A positive test does not mean the person has AIDS, although many HIV-positive people may develop AIDS in the future. Anyone who tests HIV-positive can transmit the virus to others, regardless of how long they have been infected, whether they have AIDS or other symptoms, or whether their HIV infection is being treated with antiretroviral drugs. It is extremely important that HIV-positive people follow HIV prevention guidelines, not only to protect their partners from getting HIV infection, but also to protect themselves from other germs that could cause HIV/AIDS-related disease. People at increased risk of HIV infection should NEVER donate blood, plasma, or other organs, or go to such facilities to be tested.
What is the "window period" for HIV?
It can take up to 3 months after HIV infection for enough antibodies to develop, therefore a negative test result is reliable only if the person has not had any sexual or needle-sharing risk behavior (or other exposure to infectious body fluids) during the 3 months prior to testing. Some people with recent risk behavior will test HIV antibody negative, yet may have actually been infected during the previous 3 months. Every exposure pushes the window period out another months.
Where else is HIV testing available in the community?
HIV testing is available from a variety of resources in the community:
- Private health care provider
- A Rainbow Place - 789-1780
- Nevada AIDS Foundation - 329-2437
- Nevada Hispanic Services - 826-1818
- Planned Parenthood Mar Monte - 688-5560
- HOPES - 348-1301
Who is at risk for HIV infection?
Anyone can get HIV if they have unprotected sex or share injection drug equipment with someone who is infected. The virus does not discriminate - it can infect males or females, babies, teens, adults or senior citizens. You cannot look at someone and know they have HIV. In fact, as many as 1 out of 3 people who have HIV (33%) have no idea they are infected.
Air Quality
Can I have a wood burning stove or fireplace in Washoe County?
- What is your zip code?
- What is your land-use zoning?
- What is the net size of your property?
How do I know if an air permit is required from the AQMD for my business?
Normally, a business which emits 2 pounds or more per day of criteria air pollutants or 1 pound per day or more of toxic air pollutants will require a permit to operate. Different types of air pollution control devices are also required for different processes depending upon the size of the operation for compliance with the AQMD regulations. Applications may be obtained by downloading from the District Health Department Web site. For further information, please contact one of our environmental engineers at 784-7200 for help with the necessary information for application submittal.
How do I register an air pollution complaint?
Just call 784-7200 (24 hours per day) and your complaint will be logged onto an official AQMD complaint form. After that, within "normal" hours of operation, an air quality specialist will investigate your concerns and determine if there is a violation of the AQMD regulations. If a violation exists, the person or business will be required to correct the problem. A Notice of Violation may also be issued.
Is it okay for me to burn wood in my fireplace or woodstove today?
Every year between November 1 and February 28, Northern Nevada Public Health Air Quality Management Division uses the Green, Yellow, Red Burn Code Program to inform area residents whether or not lighting stoves or fireplaces is allowed, or is advisable.
Washoe County residents can get a daily air quality update by visiting www.OurCleanAir.com or by calling the Air Quality Hotline at (775) 785-4110. They can also get this update by listening to television and radio weather forecasts, or by checking the Reno-Gazette Journal's weather page.
What are the local asbestos regulations for commercial buildings?
The local asbestos regulations essentially mirrors the federal requirements. If you own a commercial building and want to do some remodeling, an asbestos survey will need to be completed by a certified consultant to determine the presence or absence of any asbestos materials. If present, a certified abatement contractor will need to remove the asbestos before the project can proceed. In addition, the property owner will need to obtain an asbestos acknowledgment form from the AQMD prior to obtaining a building permit from the local building departments. For further information, please call 784-7200.
When does the Air Pollution Control Hearing Board meet?
The Air Pollution Control Hearing Board (APCHB) hears appeals when a negotiated resolution cannot be achieved. The APCHB meets the first Tuesday of every month (as needed).
Antimicrobial Resistance
Do antibacterial products (such as antibacterial soaps) prevent infections better than ordinary soaps?
For household use, antibacterial products are no better than ordinary soap for preventing infections. Hand washing for 15 seconds with ordinary soap and water will reduce the risk of most common infections and does not add to antibiotic resistance.
Are antibiotic-resistant bacteria a problem?
Yes. It is becoming a major public health concern. Each time you take an antibiotic unnecessarily or improperly, you increase your chance of developing drug-resistant bacteria. We could run out of ways to kill disease-causing bacteria.
You don't know who is carrying anti-biotic resistant bacteria and they may pass that resistant bacteria on to you and make you ill. This could mean stronger, more expensive antibiotics, hospitalization and, sometimes, death.
Can antibiotics be harmful?
Unnecessary antibiotics can be harmful. Antibiotics only fight bacterial infections. They do nothing to help viral illnesses like colds or influenza (flu). If you take an antibiotic when it is not necessary, such as for a cold, you increase the risk of developing an infection caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Antibiotics also destroy good bacteria in your body.
Do ear infections need antibiotics?
Sometimes. Viruses and bacteria can cause ear infections. Your doctor may wait to see if the ear infection improves by itself before deciding to give antibiotics.
Does a cold or the flu need an antibiotic?
No. The common cold and the flu (influenza) are caused by viruses, not by bacteria. Antibiotics do not work against viruses. Normal cold symptoms include sore throat, fever, cough, and/or a runny nose. A runny nose often starts out with clear drainage and then turns to a green or yellow color. This is a good sign that the body is fighting the virus. If your runny nose is not getting better after 10-14 days, please talk to your healthcare provider.
Does bronchitis need an antibiotic?
No. Viruses cause most bronchitis.
Do people become resistant to antibiotics?
No, this is a common misconception. People may exhibit allergic reactions to antibiotics, but they are not resistant to them. It is the bacteria, not the person, which become resistant.
Do sinus infections need an antibiotic?
Sometimes. Bacteria or viruses cause sinus infections. Antibiotics are needed for bacterial sinus infections. A bacterial sinus infection may be present if cold symptoms do not improve after 10-14 days.
Do most sore throats need an antibiotic?
No. Viruses cause most sore throats. Only strep throat needs an antibiotic; it is caused by strep A bacteria.
How do antibiotics work?
Antibiotics either inhibit the growth of bacteria (bacteriostatic) or actually kill the bacteria (bacteriocidal). By stopping the growth of bacteria, it gives the body time to mount an immune response and allows the body to eliminate the bacteria. Drugs that kill the bacteria are the preferred choice when someone has a weakened immune system and whose body cannot destroy the bacteria on its own. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses.
How do bacteria become resistant?
Some bacteria are naturally resistant to certain types of antibiotics. Bacteria can also become resistant by a genetic mutation or by acquiring resistance from another bacterium. Because bacteria can collect multiple resistance traits over time, they can become resistant to many different families of antibiotics, which allows the resistant bacteria to continue to live/and multiply even in the presence of antibiotic treatment.
How do I catch an antibiotic-resistant infection?
There are three ways in which you can get an antibiotic-resistant infection:
- You can develop antibiotic-resistant infections when you take an antibiotic. The bacteria could figure out how to outsmart the antibiotic and stay alive. In that case, you can transmit these resistant bacteria to others and they too may become ill.
- You can catch antibiotic resistant-infections from people or objects around you that are infected with resistant bacteria. Not properly washing hands can increase your risk of catching all kinds of infections.
- You can develop an antibiotic-resistant infection when the bacteria inside your body change; it mutates or acquires genes that allow them to resist antibiotic treatment.
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria can also develop in pigs, chickens, cattle and other farm animals, which are exposed to low doses of antibiotics in their daily feed. These resistant bacteria can then spread to humans, causing antibiotic-resistant infections. Guidelines are being developed to address this concern.
What are bacteria?
Bacteria (singular: bacterium) are one-celled organisms visible only through a microscope. There are many types of bacteria, only some of which cause disease. Most are harmless and even some are helpful (good bacteria), by aiding digestion or breaking down rotting material. Bacteria are found almost everywhere.
What can I do about antimicrobial resistance?
- Reduce the need for antibiotics.
- Wash your hands! Wash your hands! And, wash your hands! By washing your hands often and thoroughly with plain soap and water, you are helping to prevent disease and, therefore, the need for antibiotics.
- Prevent food borne illnesses by properly refrigerating perishable foods, thoroughly cooking all food from animal sources, and avoiding cross-contamination of other foods.
- Consider pets, even if not ill, as potential sources of infection.
- Dispose of feces, urine, diapers and contaminated articles properly.
Also, you should take antibiotics only when necessary. Don't insist on an antibiotic when your doctor says, "no". Never take an antibiotic for a viral infection such as cold, cough, or flu. Take an antibiotic exactly as the doctor prescribes. And take the antibiotic until it is gone, even if you are feeling better. Never save the medication to treat yourself or others later.
What can I do to feel better?
It is very important to have your body help itself. Get plenty of sleep, drink lots of fluids and eat healthy foods. Help decrease the symptoms by using a vaporizer or use over-the-counter medicines like saline nose drops, gargles or throat lozenges. Viral infections simply take time to get better.
What is an antibiotic?
An antibiotic is a powerful medication designed to kill bacteria or stop them from growing, such as an illness caused by strep throat. They cannot cure illnesses caused by viruses, such as a cold or the flu. Different antibiotics may be used for different types of bacterial infections. Your health care provider will determine what infection you have and if an antibiotic is appropriate to treat it.
What is antibiotic resistance?
Antibiotic resistance occurs when an antibiotic has lost its ability to effectively control or kill bacterial growth. These bacteria are considered to be resistant to an antibiotic. Overuse and misuse of antibiotics are the main reason for antibiotic resistance.
Birth and Death Records
How do I obtain a birth or death record/certificate?
If you are a qualified applicant, you can complete an application form and mail it along with a copy of your valid photo identification and a check or money order, payable to Northern Nevada Public Health, or you can appear in person at the office which is located in Northern Nevada Public Health, 1001 E. Ninth Street, Reno, Building B, first floor, Birth and Death Records. Our hours are listed on the Vital Statistics Program page.
Who is a qualified applicant for a birth or death record?
Birth and death certificates are confidential in the State of Nevada and may only be released to a qualified applicant. A qualified applicant is defined as the registrant, or a direct family member by blood or marriage, his or her guardian (Must provide certified original court order appointing guardianship.), or his or her legal representative. For more information, refer to NRS 440.650 and NAC 440.070.
How much does it cost for a copy of a birth or death record?
The Vital Statistics Office provides certified copies of Washoe County birth and death certificates either at the office or by mail. Fees for certified copies are set by statute and the current prices can be found on the Vital Statistics fee page.
What are the hours for Vital Statistics?
Our hours are listed on the Vital Statistics Program page.
Where can I get a copy of a birth or death certificate?
The office is located in Northern Nevada Public Health, 1001 E. Ninth Street, Reno, Building B, first floor, Birth & Death Records. Our hours are listed on the Vital Statistics Program page. For more information call (775) 328-2455.
How do I make a correction on a birth or death record?
Fill out the Affidavit For Correction of Record to amend or correct information on a birth or death record. Direct questions and send completed forms to the Nevada State Health Division Office of Vital Statistics. Adding a child's legal father to his or her birth certificate requires filling out a Declaration of Paternity form.
Commercial Recycling
Isn’t commercial recycling limited by city franchise agreements?
No. In fact, commercial recycling has been excluded from franchise agreements to allow for private enterprise to expand recycling opportunities.
How do I prepare my waste for recycling?
Waste that is to be sent for resource recovery or recycling must be separated at the site of generation. For example, if your business generates glass and aluminum cans and you want to recycle it, the glass and aluminum must separated from your other solid waste. Once separated, the recyclable materials (e.g., glass and aluminum cans) must be placed in a container for collection by a waste hauler permitted to collect and transport recyclable materials.
Is there a cost to recycle?
There is no easy answer to this question. Recyclable materials are subject to the same supply and demand limitations faced by most businesses. Flux in the market for recyclable materials has a major impact on their value. Some recyclable materials have enough value that a permitted waste hauler will collect them for free or even pay for the material. Other recyclable materials may have a low value, requiring the permitted waste hauler to charge you a nominal fee to collect them. As with most resources, collection and transportation costs may offset any profit that could be realized from recycling.
Where can I get more information if I am interested in establishing a recycling program for my business?
For more detailed information, please contact Northern Nevada Public Health, Environmental Health Services Division at (775) 328-2434. The staff assigned to the Waste Management Program can answer your questions and provide more information.
Additional materials on waste reduction and proper waste management (including hazardous waste) can be obtained from the University of Nevada, Reno Small Business Development Center, Business Environmental Program.
What can be recycled?
Any waste material that has an end use or can be re-processed into a usable material, product or item. This includes, but is not limited to, food waste, aluminum, glass, yard debris, plastic, office paper, etc. Additionally, this includes any solid waste that can be processed and used as a feedstock for energy generation. Not all recyclable materials can be recycled in Washoe County due to lack of markets, availability of necessary collection services, etc. Prior to recycling any material, it is important to identify the method of transportation and the final processing location.
Why recycle if the process will cost my business money?
There are environmental benefits to recycling that are well documented. For example, paper recycling has greatly reduced the need to harvest virgin timber to make paper products. Instead, waste paper is re-processed and used in the manufacturing of new paper. Thus, the act of recycling promotes efficient and cost effective use of solid waste without depleting limited natural resources. This effort also limits environmental degradation that often results when extracting or harvesting virgin raw materials.
Another benefit can be realized by promoting the fact that your business recycles. Sustainability, responsible use of resources and commitment to community can be featured as part of an advertising campaign. Further, many residents are demonstrating a preference for businesses that actively recycle. Finally, by reducing the overall amount of waste that must be disposed, your business may reduce the cost for disposal. For example, if a business currently uses a six (6) yard dumpster, but can divert 20 – 30% of their waste to recycling, a four (4) yard dumpster would be adequate, resulting in lowered cost for service to the dumpster.
Cottage Food
Are there production limits for my Cottage Food Business?
The Nevada Legislature (SB 206 77/2013) placed a $35,000.00 per year limit to the amount of money that one can earn in the Cottage Food Industry.
Can I give out Cottage Food samples?
You can give out samples if they are prepackaged and labeled per the Cottage Food and Food Safety Guidelines.
Can I sell Cottage Foods over the phone or the Internet?
No, you may not sell Cottage Foods over the Internet or the phone. All sales must occur by means of an in-person transaction. Shipping product through the mail is prohibited. You may have a website/social media account that has your business information, but all sales must be conducted by the customer contacting you.
Can I sell my Cottage Foods to a wholesaler, etc.?
No, your foods are not inspected/produced under the required industry standards. The Cottage Food law disallows this.
Do I need to obtain a Business License for Cottage Foods?
Contact the following Business License Departments:
- Washoe County (775) 328-3733
- City of Reno (775) 334-2090
- City of Sparks (775) 353-2360
Do I need a Health Permit to sell Cottage Foods?
No, but you need to be registered with a Nevada jurisdicion to sell in Washoe County. To sell in other Nevada Counties you must contact the respective agencies to enquire about registration procedures and policies.
- Carson City Health and Human Services - (775) 887-2190
- Southern Nevada Health District - (702) 759-0588
- All other rural areas - Nevada Department of Health and Humans Services - (775) 687-7533
Do I need to collect Sales Tax for Cottage Foods?
Please visit the Nevada Department of Taxation for further details.
How do I file a complaint against a Cottage Food operation?
Contact your local Health District. Northern Nevada Public Health (775) 328-2434
- Carson City Health and Human Services- (775) 887-2190
- Southern Nevada Health District- (702) 759-0588
- All other rural areas - Nevada Department of Health and Humans Services- (775) 687-7533
Must I put a label on my Cottage Foods?
Yes, see the Cottage Food Fact Sheet and Food Safety Guidelines for details.
Why can’t I sell Cottage Foods to my favorite restaurant, etc.?
Your foods are not inspected/produced under the required industry standards (USDA, FDA) that are required for routine sales/use to the food service industry. The Cottage Food law disallows this.
What foods may we not sell as Cottage Foods?
Home canned foods and sauces, pickled items, breads/cakes/pies made with home canned food ingredients, apple cider, dried or dehydrated meats or chicken (jerkies), apple (fruit) butters, pumpkin butter or other fruit butters. Additionally, foods containing cream cheese frosting, uncooked egg, custard or meringue may not be sold.
What types of Cottage Foods may I produce?
Breads, cakes, pastries, candies, cookies, bread mixes, fruit pies, jams, jellies, preserves, dried fruits, popcorn, popcorn balls, cotton candy, dry herbs, seasonings, cereals, trail-mixes, granolas, coated and un-coated nuts and vinegar and flavored vinegar.
Where can I find a copy of the Cottage Food Law?
Where may I sell my Cottage Foods?
In your home, at a roadside stand on your own property, flea market, swap meet, church bazaar, garage sale or craft fair.
Why are some products not allowed to be sold as Cottage foods?
This is due to the inherent risks that may be associated with these non-allowable foods, since they will not be inspected or regulated by Local/State/Federal health officials. The bill passed by the Nevada Legislature allowed only certain listed foods to be provided.
E. coli
How does a person get E. coli?
One way E. coli can be contracted is when a person eats food that has been contaminated with animal waste or unsanitary water.
How long will it take for me to get well from E. coli?
Symptoms usually resolve within five to 10 days.
How sick can E. coli make me?
In some people, particularly children under five years of age and the elderly, the infection can also cause a complication called hemolytic uremic syndrome, in which the red blood cells are destroyed and the kidneys fail. About two to seven percent of infections lead to this complication. In the United States, hemolytic uremic syndrome is the principal cause of acute kidney failure in children, and most cases of hemolytic uremic syndrome are caused by E. coli O157:H7.
What are the symptoms of E. coli?
The main symptom is diarrhea, which is often bloody, accompanied by abdominal cramps. There also can be a mild fever.
What is E. coli O157:H7?
E. coli O157:H7 is one of hundreds of strains of the bacterium Escherichia coli. Although most strains are harmless and live in the intestines of healthy humans and animals, this strain produces a powerful toxin and can cause severe illness.
When should I see a doctor?
If you have severe, prolonged or bloody diarrhea, you should seek medical attention.
Environmental Health
Where do I make a complaint if I become sick from eating food at an event or restaurant?
If you believe that you became ill as a result of eating a meal prepared at a food establishment located in Washoe County, please call our office at (775) 328-2434 to report your illness.
Do I need a permit to drill or recondition an existing well?
A well construction permit must be obtained from Northern Nevada Public Health to construct, drill, deepen or plug a well. Well construction permits can be applied for via our online permitting portal www.OneNV.us. Please refer to our Well Permitting Requirements (English) (Spanish) for the minimum requirements for all well construction permits. Additional items may be required based on site conditions.
Family Planning Clinic
Does the Family Planning clinic have staff that speak Spanish?
Yes. We have staff that speak Spanish and interpret in the clinic. We also have a telephone interpreting service that can assist with interpretation in many other languages.
Where is the Family Planning Clinic located?
The Health Department is located at the corner of 9th Street and Wells Ave., just off the freeway and next to the fairgrounds. The address is 1001 East 9th Street, Building B. If you are traveling North on Wells, the entrance to the clinic is the first right (into the parking lot) after passing 9th Street. You can enter the door marked CLINIC SERVICES.
How do I pay for my Family Planning Clinic visit?
We accept cash, check, money orders and credit cards.
Is the Family Planning clinic appointment confidential?
Yes. All appointments are confidential.
Is there a bus stop near the Family Planning clinic?
Yes. There are Citifare bus stops close to the Health Department along routes 2 and 12.
I'm pregnant and thinking about adoption, where can I go to find out more information?
Social Services has information on adoption.
I just had sex and didn't use protection. I don't want to get pregnant. What can I do?
If you take an Emergency Contraception (the Plan B pill) within five days of unprotected sex you can reduce your chance of pregnancy by up to 75%. You need to be seen by a nurse to receive this medication. Call the clinic ASAP to make an appointment. For weekend, holiday or evening emergency contraception providers in the local area dial 1-888-NOT-2-LATE.
I've been sexually assaulted and I am afraid to tell the police. What do I do?
Contact Sexual Assault Support Services Crisis Call Center at 784-8090 or 1-800-992-5757 and they will listen to you as well as give you information about resources in the community that may help.
What ages of women do you see in the Family Planning clinic?
We see women in their reproductive years, which means during the time in their lives when they are able to have children. When a woman reaches menopause (stops having her period) we refer her to a different clinic for annual exams.
What is a Pap smear?
A Pap smear is a test that looks for changes of the cells on the cervix. If you would like to know more, please see the Pap Smear information sheet.
I am pregnant so where do I go to get checked (prenatal care)?
- We provide pregnancy testing and proof of pregnancy if your test is positive. We do not provide prenatal care services: however, we will tell you where to receive those services.
- The Washoe Pregnancy Center provides prenatal care services on a sliding scale. Their phone number is (775) 982-5640.
Immunizations
Can grandparents bring their grandchildren in for their vaccinations?
A parent or legal guardian must be the person who receives the vaccine information sheet (VIS), HIPAA informational sheet, HIPAA consent form and completes the vaccine administration record for the child receiving shots. Vaccine Information Sheets (VIS).
Before we moved to Nevada, my doctor said my child's immunizations were up to date. Why is my school now telling me my child needs more shots?
States have different requirements for school entry. The following are required by Nevada State Law:
- Tdap - All students entering 7th Grade must have a Tdap.
- Varicella - Students new to Nevada schools, who have not had Chicken Pox Disease, must have two (2) Varicella doses. The second dose must be at four (4) years of age or older.
- Polio - Students new to Nevada schools must have four (4) doses of Polio. The 4th dose must be at four (4) years of age or older.
Will the Health District bill my insurance company for immunizations?
NNPH only bills Medicaid, Nevada Check-up, and Cigna. You will be provided a receipt to submit to your insurance company with your claim for reimbursement.
How will I know when my child needs more shots?
Many shot records indicate when the next vaccinations are due. Parents can check with their physician's office or clinic. Complete childhood and adult immunization schedules are available at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/imz-schedules/index.html. Annual influenza (flu) vaccination is recommended for children aged 6 months or older.
Will I need an appointment for an immunization or can I just come to NNPH?
Appointments are required for immunizations. We make appointments up to one week in advance. Walk in appointments are limited to schedule openings.
Salmonellosis
How common is Salmonellosis?
- About 40,000 cases are reported in the United States each year (actual number may be significantly higher, as many milder cases are not diagnosed or reported.
- About 400 people with acute Salmonella die each year.
- It is more common in the summer than in the winter.
- Children are the most likely to get Salmonella.
How is Salmonellosis diagnosed?
Through fecal specimens sent to a testing laboratory.
How is Salmonellosis transmitted?
Through the feces of people or animals including birds and especially reptiles (this includes turtles) to other people or animals, usually through food that has been contaminated, either though direct contact with infected feces or through unwashed hands of an infected food handler (did not wash hands after using the bathroom).
How is Salmonellosis treated?
- Most infected persons recover without treatment unless the person becomes severely dehydrated.
- Antibiotics usually are not necessary unless the infection spreads beyond the intestines.
How long does a person infected with Salmonellosis stay ill?
Usually five to seven days.
How long does the Salmonellosis bacteria survive in the environment?
It depends on environmental conditions.
How sick can a person infected with Salmonellosis get?
- Most infected persons recover without treatment.
- Some develop severe diarrhea, leading to dehydration and hospitalization for rehydration with intravenous fluids.
- In some cases, the infection can spread from the intestines to the bloodstream, then to other body sites. In these cases, death can result unless the infected person is treated promptly with antibiotics.
- A small number of people go on to develop Reiter’s syndrome (pains in joints, irritation of the eyes and painful urination), which can last for months or years and can lead to chronic arthritis.
- Young children, the elderly and the immunocompromised are the most likely to have severe infections.
What are steps for avoiding disease transmission/getting Salmonellosis?
- Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent Salmonella.
- The primary method of prevention is to thoroughly wash your hands
- After using the bathroom
- After having contact with animal feces
- After handling reptiles or birds
- Avoid cross-contamination by
- Thoroughly washing your hands before handling any food and between handling different types of food
- Keeping uncooked meats separate from produce, cooked foods and ready-to-eat foods
- Thoroughly wash hands and cutting boards, counters, knives and other utensils used to prepare uncooked foods of animal origin.
- Do not eat or drink raw or undercooked foods of animal origin (e.g., eggs, poultry or meat or unpasteurized milk).
- Thoroughly wash produce before eating.
- If you have Salmonella, do not prepare food or pour water for others until you have been shown to no longer be carrying the Salmonella bacterium.
Is Salmonellosis required to be reported to health authorities?
Yes.
What are the symptoms of Salmonellosis?
Diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps.
What is Salmonellosis?
Salmonellosis is an illness with symptoms that usually begin in the intestines. It is caused by a bacterium called Salmonella.
How long does it take for Salmonellosis test results to be available?
At least 72 hours, as testing involves growing a culture.
What is the incubation period (the time from exposure to Salmonellosis until the time symptoms occur)?
Symptoms develop within 12 to 72 hours after infection.
Where can I get more information on Salmonellosis?
- Log onto www.cdc.gov/salmonella or www.fda.gov
- Locally, calls can be directed to 775.328.2447
Smoking Ban
Are businesses in Washoe County complying with the NCIAA?
Staff from the Environmental Health Services Division of the Health District have been conducting smoking ban compliance surveys during routine inspections since December 19, 2006. To date, an average 96.5% of permitted facilities were in compliance with the requirements set forth in the NCIAA during routine Environmental Health Services permit inspections.
Can a business allow smoking during certain times of the day?
No. The NCIAA states: "Smoking tobacco in any form is prohibited within indoor places of employment including, but not limited to, the following:
- Child care facilities;
- Movie theatres;
- Video arcades;
- Government buildings and public places;
- Malls and retail establishments;
- All areas of grocery stores; and
- All indoor areas within restaurants."
There are no provisions for allowing smoking, at any time, in any of the above locations.
Four ways to ask smokers to "take it outside":
Asking strangers, and sometimes even friends and family, to smoke outside can sometimes be stressful. It is important to remember that the vast majority of people are respectful and will abide by the law, if they are aware and reminded of it. Below are 4 ways to ask people who smoke to "take it outside". It may not be easy at first but you have the right and the responsibility to avoid secondhand smoke.
- As the business owner/manager to enforce the law: I thought this was a non-smoking business. Would you please ask them to smoke outside?
- Remind them of the law: Maybe you didn't know, but Nevada law prohibits smoking in this area/building/business. Smoking is allowed outside.
- Be polite: I would like to ask a favor. Would you mind smoking outside? This is a non-smoking area.
- It is the smoke, not the smoker that is the problem: Would you not smoke right now? I`d really appreciate it.
How do I comply with the NCIAA if I am a childcare facility?
Please see the guide for childcare facilities for information on compliance.
How do I comply with the NCIAA if I am an employer?
Please see the guide for employers for information on compliance.
I smoke, so how does the NCIAA apply to me?
Smokers play an important role in helping to implement the law. First and foremost, it is now illegal for you to smoke indoors in a facility where smoking has been banned. Even if a "No Smoking" sign is not displayed there, you are still required by law to refrain from smoking. You should also not bring any ashtrays or items used as ashtrays into a facility where smoking is now banned. You may still smoke anywhere outside of a facility where smoking is now banned indoors. You may also still smoke indoors at the following types of businesses:
- Areas within casinos where loitering by minors is already prohibited by state law;
- Stand-alone bars, taverns, and saloons that do not require a permit to serve food;
- Strip clubs and brothels;
- Retail tobacco stores;
- Private residences, including those which may serve as an office workplace, except if used as a childcare, an adult day care, or a health care facility; and
- Hotel and motel rooms, but only if allowed by the facility operator, so please ask the operator first before smoking there.
If you are uncertain about being able to smoke indoors, please ask the owner and/or manager of the facility first before smoking there. Your compliance with the new law helps protect non-smokers and children from the dangers of secondhand smoke. Your compliance also helps merchants meet their responsibilities under the new law. If you are asked by a representative of the business to refrain from smoking inside their facility, please do as they ask. It is the business's responsibility to enforce the new law in their establishment; if you are found smoking indoors at a location where smoking is now banned, then the business itself could be cited and required to pay a fine. You, too, could be found guilty of a misdemeanor, which generally carries a fine imposed by a judge. A person who violates this ban is also liable for a civil penalty of $100 for each violation.
How have smoking bans in other communities affected business owners?
Banning smoking in indoor spaces has been shown to have a positive impact for business owners in addition to the general community. Studies have shown that banning smoking in restaurants and bars can boost revenues and increase employment. For example, taxable sales receipts for bars and restaurants have increased every year in California since their smoking ban took effect in 2002. In New York City, tax receipts for restaurant and bars increased 8.7 percent, and employment increased by 10,600 jobs since their 2003 smoking ban went into effect; and, in Florida, retail sales for restaurants, lunchrooms, and catering services increased by 7.3 percent after a 2003 smoking ban. Florida's sales and employment in the hotel, restaurant, and tourism industries also were not hurt. Smoking bans in places of employment also have been shown to lower employee sick leave usage, health insurance costs, fire insurance rates, and cleaning costs.
Many studies have been conducted about the business impact of indoor smoking bans. For more information about these studies, please visit: tobacco.ucsf.edu.
How will the NCIAA be enforced?
Compliance with the ban is the responsibility of the owner, manager or operator of an area where smoking is prohibited. A reasonable effort to prevent smoking should be made by this individual or group of individuals. Health authorities, police officers of cities or towns, sheriffs and their deputies shall, within their respective jurisdictions, enforce the provisions of the ban and shall issue citations for violations of the ban.
How will the NCIAA improve the health of Washoe County?
Exposure to secondhand smoke has been linked to numerous life-threatening diseases such as heart attack, stroke, and cancer. Eliminating smoking in indoor spaces reduces exposure to secondhand smoke, thereby reducing the occurrence of these chronic illnesses. Research in communities that have implemented indoor smoking bans shows significant improvement to public health after the ban goes into effect. For example, hospital admissions for heart attacks dropped 40 percent in the six months following an indoor smoking ban in Helena, Montana; and, in Pueblo, Colorado, heart attacks declined 30 percent in 18 months after smoking was banned indoors.
Where can I get information about tobacco and secondhand smoke?
For information about tobacco and secondhand smoke, please visit the Be Tobacco Free page or call (775) 328-2442.
Where can I get information on quitting smoking?
If you smoke and want to quit, see the list of local stop smoking programs.
What if I have more questions about the NCIAA?
Please contact Environmental Health Services at 775-328-2434 with any questions you may have about enforcement and compliance.
For questions about the public health impact of the ban, call 775-328-2442.
What will it cost business owners to comply with the NCIAA?
The cost to comply with the law will vary for each business, but, in general, there are minimal costs. Employers must clearly and conspicuously post "No Smoking" signs in their facilities at every entrance. They also are required to remove all ashtrays and other smoking paraphernalia from any area where smoking is prohibited. For some businesses, additional costs may be associated with the removal of built-in ashtrays or other smoking-related items.
What are the penalties of violating the NCIAA?
A person who is found to violate the ban is guilty of a misdemeanor, which generally carries a fine imposed by a judge. In addition, a person who violates this ban is liable for a civil penalty of $100 for each violation.
Whom do I contact to complain about smoking violations?
Please contact Environmental Health Services at 775-328-2434.
What changes does the NCIAA make?
As a result of the voters' mandate, smoking tobacco in any form now is prohibited within indoor places of employment, including, but not limited to: childcare facilities, movie theatres, video arcades; government buildings and public places; malls and retail establishments; all areas of grocery stores; all indoor areas within restaurants; and within school buildings and on school property.
Smoking tobacco is not prohibited in areas within casinos where loitering by minors is already prohibited by state law; stand-alone bars, taverns, and saloons that do not require a permit to serve food; strip clubs and brothels; retail tobacco stores; private residences, including those which may serve as an office workplace, except if used as a childcare, an adult day care or a health care facility; and hotel and motel rooms, if allowed by the facility operator.
For more information on the smoking and tobacco laws in Nevada, refer to Nevada Revised Statute (NRS) 202.2483.
What is smoking-related paraphernalia?
Ashtrays or any items being used as an ashtray (e.g., beer bottles, coffee mugs, discarded trash, etc.) are considered smoking-related paraphernalia and must be removed from any area where smoking is prohibited. Merchants may still sell tobacco products.
When did the NCIAA go into effect?
The Nevada Clean Indoor Air Act (NCIAA), became statewide law on December 8, 2006.
Where can I get a printable no smoking sign?
If the law refers to "public places," then why is smoking banned in businesses that are privately owned?
Sec. 2 (9) (d) of the new law defines "public places" as "any enclosed areas to which the public is invited or in which the public is permitted." If a business meets this definition, then smoking must be banned there indoors, regardless of how the facility is owned. The law also defines a "place of employment" in Sec. 2 (9) (i) as "any enclosed area under the control of a public or private employer which employees frequent during the course of employment including, but not limited to, work areas, restrooms, hallways, employee lounges, cafeterias, conference and meeting rooms, lobbies and reception areas." Again, if a business meets this definition, then smoking must be banned indoors as described, regardless of how the facility is owned. The law does make an exception in Sec. 2 (3) (e) for private residences that serve as workplaces, except if they are being used as a childcare, adult day care, or health care facility.
Why is the Health District involved in the NCIAA?
Sec. 2 (7) of the new law states that "Health authorities, police officers of cities or towns, sheriffs and their deputies shall, within their respective jurisdictions, enforce the provisions of this Act and shall issue citations for violations of this Act[.]" The Northern Nevada Public Health is the health authority for Washoe County (per NRS 202.2485). Therefore, Northern Nevada Public Health is required by law to enforce the smoking ban.
Why was the NCIAA passed?
The ban was passed in order to protect the public from secondhand smoke. Secondhand smoke, also called environmental tobacco smoke, is a combination of smoke from the burning end of a cigarette, cigar or pipe and the smoke exhaled by smokers.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reports that secondhand smoke contains more than 4,000 substances, many of which are known to cause cancer in humans. In 2006, the U.S. Surgeon General released a comprehensive report stating that there is no risk-free level of secondhand smoke exposure.
Solid Waste Management Plan
What if I don't understand some of the terms in the Solid Waste Management Plan?
There is a glossary in the beginning of the Plan. The EPA website also has a helpful glossary of terms at http://www.epa.gov/OCEPATERMS/.
What is solid waste?
Solid waste is anything you would throw away or discard such as garbage or trash.
Special Events/Temporary Food
Is there an annual permit to cover a full season for temporary foods?
Yes! We offer three annual permits:
- Annual Sampling Permit: For vendors only providing individual sample portions of food/beverages.
- Annual Producer Permit: For vendors selling packaged agricultural products like nuts, eggs, USDA-stamped meat, and other agricultural items.
- Annual Itinerant Vendor Permit: For vendors participating in eight or more events per year. This permit allows unlimited event participation within the year, with a limit of 14 dates per single event. Additional equipment and a servicing area are required.
These permits are valid only for the calendar year in which they are purchased.
If I turn in a food permit application and pay the fee, have I been approved?
No. The application is subject to review and food service operations must comply with regulations. Incomplete applications may be rejected. Applications may also be rejected based on inability to contact the person in charge of food service, menu item restrictions, or operational concerns.
I am going to buy bulk muffins and bagels at my local grocery store and sell them individually at an event. Do I need a temporary food permit?
If food items that are not individually prepackaged and on-site preparation (opening of package and contact with food item) is required, a temporary food establishment permit must be obtained.
Can I prepare food for a Special Event at home?
Only registered cottage food operators can prepare food at home for a special event. All cottage food requirements must be followed including packaging and labeling requirements. Other than the above exception, no food preparation is allowed at a private residence for items served to the public.
All preparation of food for a special event must be conducted at the event or in a pre-approved permitted food establishment.
What is a cumulative maximum fee for special events/temporary food establishments?
A temporary food establishment which operates at the same special event, in the same location and serves the same menu for at least three times during a calendar year will be eligible for a cumulative maximum fee. The temporary food establishment will be charged the permit fee for the event multiplied by three. The operation of the temporary food establishment is limited to 14 days per calendar year.
Do I still need a permit if I am giving away food?
What food and beverage items are exempt from permit requirements?
- Bottled water, canned soft drinks.
- Coffee/Tea with powdered non-dairy creamer or ultra-pasteurized creamer packaged in individual servings (this exemption does not include beverages such as lattés and espressos that are mixed with dairy product or ice by the vendor during preparation).
- Commercially prepared acidic beverages (orange juice, lemonade, etc.) that are served from the original, properly labeled container without the addition of consumer ice or other regulated food product.
- Draft beer and other alcoholic beverages (wine) that are served without the addition of consumer ice or the addition of other regulated food product.
- Hermetically sealed and unopened containers of non-time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) etc.
- Hot chocolate prepared without the use of time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) dairy products.
- Non-time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) prepackaged baked goods with proper labeling from an approved source and requiring no on-site preparation (opening of package and contact with food item).
- Non-time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) and unopened prepacked foods from an approved source with proper labeling such as honey, jerked meats, potato chips, popcorn and other similar foods.
- Produce sold from a produce stand where no sampling (cuttin or slicing) or food preparation is done.
- Commercially prepared, prepackaged, and unopened ice cream that is appropriately labeled as to ingredients and manufacturer. Smoothie products (Jamba Juice and Keva Juice) made and prepackaged at the fixed permitted facility and appropriately labeled with ingredients and manufacturer.
- Shelled and unshelled nuts, including flavored nuts for sample or sale.
- Food Supplements that are offered for sample or sale without the addition of regulated food items. These include, but are not limited to vitamins, minerals, protein powder mixes, energy drinks, and herbal mixtures (excluding those containing unapproved additives such as CBD or kratom).
- Foods from an approved source prepared for a “cook-off” or judging contest in which food is not provided to the public.
Can I sell food made from a private home at my school or church fundraiser?
Yes. A religious, charitable or other nonprofit organization may, without possessing a permit from Northern Nevada Public Health (NNPH), sell food to raise money, whether or not the food was prepared at a private home, if the sale occurs on the premises of the organization.
Is there a food permit fee exemption for veterans as in California?
No. County Finance has not passed any such exemptions for purchase of permits.
I am a grocery store and I would like to barbeque food outside and sell/serve the food inside. Do I need a temporary food permit?
No. If a fixed facility (grocery store, restaurant, etc.) already has a permit through Northern Nevada Public Health (NNPH) Food Protection Program, and the food will be sampled inside the store, a temporary food permit is not required. If the establishment wishes to sample or sell food outside, a temporary food permit is required.
I am a grocery store and I would like to sample food inside my store. Do I need a temporary food permit?
No. If a fixed facility (grocery store, restaurant, etc.) already has a permit through Northern Nevada Public Health (NNPH) Food Protection Program, and the food will be sampled inside the store, a temporary food permit is not required. If the establishment wishes to sample or sell food outside, a temporary food permit is required.
How far ahead of time must I purchase a Temporary Food Permit?
A temporary food permit must be obtained at least seven (7) calendar days prior to the event. Late fees apply to applications submitted within seven (7) days prior to the event.
I am an existing food establishment that would like to participate in a special event what do I do?
Existing food establishment permits do not extend outside of the approved fixed facility. Existing food establishments must obtain a Temporary Food Permit when operating outside of the approved facility.
I have a mobile food unit and would like to participate in a special event. Do I need a temporary food establishment permit?
I am going to have a tasting event where food is donated and sampled by patrons; do I need a temporary food permit?
A temporary food establishment permit must be obtained to cover each separate food vendor. Please contact this agency for available permitting options.
Can I prepare the food for a Special Event ahead of time at an approved facility?
Any food prep performed prior to the first day of a special event must receive prior approval from the NNPH. Advanced preparation details must be disclosed in the temporary food permit application. Cooking and cooling of food items in advance is usually not allowed.
I am a promoter and I would like to organize and put on a special event, what do I need to do?
The promoter must first contact the city or county business licensing department (Washoe County, City of Reno or City of Sparks) in which the event is going to be held to ensure the necessary permits/licenses are obtained in order to operate within the city/county limits. If the event’s daily attendance is equal to or exceeds 5,000 persons per day, or the total attendance over a fourteen (14) day period is equal to or exceeds 10,000 persons, the promoter must obtain an Application for a Special Event Permit from Northern Nevada Public Health.
Is there a reduced food permit fee for non-profits?
No. Non-profit fees were removed from the current fee schedule as of July 1, 2016.
What is a low risk food?
Examples of low risk food items include, samples given of any food item (including potentially hazardous foods), any beverage served in an open container with consumer ice, coffee drinks blended with dairy products (espresso, lattés), popcorn, pretzels, cotton candy, snow cones/shaved ice, funnel cakes, French fries, fried/cooked vegetables, roasted corn, churros, breads, pastries, nuts, sliced fruit (including melons), candy, fudge/chocolate.
What is a time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) food?
Time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) food includes any animal food (a food of animal origin) that is raw or heat-treated; a food of plant origin that is heat-treated or consists of raw seed sprouts; cut melons; and garlic-in-oil mixtures that are not modified in a way that prevents bacterial growth. Some examples of time/temperature control for safety food (TCS) food include, meat, poultry, fish, shell fish and crustaceans, milk and dairy products, cooked rice, and cooked beans, baked potatoes, tofu and soy protein foods, eggs (except those treated to eliminate Salmonella), raw sprouts, sliced melons, cut tomatoes, and cut leafy greens.
What is a special event?
A special event is a transitory gathering such as, but not limited to, an activity (including soccer, pickleball, baseball and softball league games), a celebration, festival or fundraiser which is open to the public.
What is a temporary food establishment?
A temporary food establishment is any food establishment which operates at a fixed location for a temporary period of time, not to exceed 14 consecutive days, in connection with a special event.
STD
What communicable diseases am I required to report?
In regards to STDs, what diseases am I required to report?
Teen Health Mall
Does the Teen Health Mall have staff that speak Spanish?
Yes. We have staff that speak Spanish and interpret in the clinic. We also have a telephone interpreting service that can assist with interpretation in many other languages.
Is there a bus stop near the Teen Health Mall clinic?
Yes. There are Citifare bus stops close to the Health Department along routes 2 and 12.
Is the Teen Health Mall appointment confidential?
Yes. All appointments are confidential.
I'm pregnant and thinking about adoption, where can I go to find out more information?
Human Services Agency has information on adoption.
I just had sex and didn't use protection. I don't want to get pregnant. What can I do?
If you take an Emergency Contraception (the Plan B pill) within five days of unprotected sex you can reduce your chance of pregnancy by up to 75%. You need to be seen by a nurse to receive this medication. Call the clinic ASAP to make an appointment. For weekend, holiday or evening emergency contraception providers in the local area dial 1-888-NOT-2-LATE.
I've been sexually assaulted and I am afraid to tell the police. What do I do?
Contact Sexual Assault Support Services Crisis Call Center at 784-8090 or 1-800-992-5757 and they will listen to you as well as give you information about resources in the community that may help.
Where is the Teen Health Mall Clinic located?
The Health Department is located at the corner of 9th Street and Wells Ave., just off the freeway and next to the fairgrounds. The address is 1001 East 9th Street, Building B. If you are traveling North on Wells, the entrance to the clinic is the first right (into the parking lot) after passing 9th Street. You can enter the door marked clinic services.
What does it mean to receive family planning services?
The Teen Health Mall offers family planning services to help you plan the size of your family. By using birth control methods a woman has more control over when she has children and how many children she has.
What do I need to bring to my first Teen Health Mall visit?
- If it is your first visit, or if your income has changed, please bring proof of family income. Please see Cost of Services.
- If you are on medications, bring in your medications, or write down the names so a nurse can review them. This would also include any birth control pills that you did not receive from this clinic.
What is a Pap smear?
A Pap smear is a test that looks for changes of the cells on the cervix. If you would like to know more, please see the Pap Smear information sheet.
What is the Teen Health Mall phone number?
The number to the office clinic is (775) 328-2470. The phones are answered between the hours of 9 a.m. - noon and 1 p.m. - 4 p.m.
What will happen at my first Teen Health Mall visit?
- You will fill out paperwork.
- An aide will obtain your weight and height, measure your blood pressure, and check your iron level (in some cases).
- The Advanced Practitioner of Nursing will review your medical history and determine what services you need (birth control, STD testing etc.).
- If you are interested in birth control you may get it on the day of your visit; however, in some instances you will need to return to receive your method of birth control.
- You may or may not receive a pelvic exam (having a nurse look and feel inside your vagina) and Pap smear on your first visit. If you receive birth control you will need to have a pelvic exam within 3 months.
When do I pay for the Teen Health Mall visit?
You can pay for your visit on the day that you receive services, or we can put you on a payment plan.
I am pregnant so where do I go to get checked (prenatal care)?
- We provide pregnancy testing and proof of pregnancy if your test is positive. We do not provide prenatal care services: however, we will tell you where to receive those services.
- The Washoe Pregnancy Center provides prenatal care services on a sliding scale. Their phone number is (775) 982-5640.
Tuberculosis (TB)
What if I had Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) vaccination for TB?
Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) is a vaccine for tuberculosis. It is often given to infants and young children in countries with high rates of tuberculosis. It protects children and babies from developing severe forms of tuberculosis, like meningitis or miliary TB. It is not used routinely in the United States. Your skin test may be positive because of BCG vaccination.
However, a positive skin test is most likely due to infection with TB bacteria if:
- You recently spent time with a person who has active TB disease
- You are from an area of the world where active TB is very common (Africa, Latin America, Asia, Eastern Europe and Russia)
- You spend time where TB disease is common (homeless shelters, migrant farm camps, drug treatment centers, health care clinics. jails or prisons)
- You were vaccinated more than 5-10 years ago
- Your skin test is greater than 20 mm
Consider a blood test. Blood tests are not affected due to BCG - they will not give a false positive result due to BCG.
What is the difference between latent TB infection and TB disease?
A Person with Latent TB Infection (LTBI):
- Usually has a skin test or a blood test result indicating TB infection*
- Usually has a normal chest x-ray
- Has TB bacteria in their body that are alive but inactive
- Has no symptoms
- Does not feel sick
- Cannot spread TB to others
- Can take treatment for LTBI to reduce their risk of developing TB disease
A Person with Active TB Disease:
- Usually has a skin test or a blood test result indicating TB infection*
- Usually has an abnormal chest x-ray
- Has TB bacteria in their body that are active (growing)
- Usually feels sick and experiences symptoms
- May spread TB to others
- Needs treatment to cure the active TB disease
* - A positive tuberculin skin test (TST) or a positive blood test only shows that you have been infected with the TB bacteria. Neither test can tell if you have TB disease, only if the TB bacteria are in your body.
How is latent TB infection treated?
Treating latent TB infection is essential to controlling and eliminating TB in the United States, because it substantially reduces the risk that the infection will progress to TB disease.
A person with TB infection can take medication called Isoniazid or Rifampin. This will kill the TB bacteria and greatly reduce the risk of TB disease from developing. Your doctor will decide which medicine is best for you. It is important to have health monitoring every month while taking either of these medications to be sure that you are not developing any harmful side effects. Your health care provider may order blood tests during your treatment.
There is now a 12 dose regimen that makes treating latent TB infection easier.
Considered one of the biggest breakthroughs in treatment for latent TB infection (LTBI) since the 1960s, the 12-dose regimen reduces treatment from 270 daily doses over 9 months, to 12 once-weekly doses over 3 months. It is a combination regimen of isoniazid and rifapentine; two of the most effective medications available for TB treatment.
Following the results of a recent large randomized control trial, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) released recommendations on the use of the new treatment regimen for LTBI:
- It is recommended for otherwise healthy people aged 12 and older who are at an increased risk of developing TB disease
- Close patient monitoring and the utilization of Direct Observed Therapy (DOT) in which a health care worker observes a person taking the treatment and monitors side effects is required for each of the 12 doses
- It is an additional treatment option for LTBI and is not meant to replace other available treatment regimens
How is TB disease treated?
It takes a long time to kill all the TB bacteria. A person with TB disease typically must take 4 different medicines for 2 months:
- Isoniazid
- Rifampin
- Pyrazinamide
- Ethambutol
Then take Isoniazid and Rifampin for another 4-7 months depending on how much damage the bacteria have caused.
This treatment has been successful in treating TB disease for many years. In recent years, some TB bacteria strains have become resistant, (the medicines no longer kill the TB bacteria) to one or more of these drugs.
Multi-drug resistant (MDR) TB is resistant to the two strongest TB medicines, Rifampin and Isoniazid. The most common cause of drug resistance occurs when TB medications are not taken long enough and/or in the right amounts. Drug resistant TB is much more difficult and expensive to successfully treat. Extremely drug resistant (XDR) TB is a less common form of multi-drug resistant TB. There is resistance to Isoniazid and Rifampin, as well as most of the alternative drugs used against MDR TB. The Center for Disease Control and Prevention urges all health care practitioners to use directly observed therapy (DOT) in the treatment of tuberculosis.
How is TB spread?
When a person with active TB disease coughs or sneezes tiny droplets that contain TB bacteria are released into the air. If another person breathes air containing these droplets, they may become infected with the TB bacteria. However, not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick. As a result, two TB-related conditions exist: Latent TB infection (LTBI) and Active TB disease - both of which are treatable and curable.
My TB test is positive, now what?
You will need to have a chest x-ray. If your chest x-ray is normal, this means you have been infected with the TB bacteria but your immune system has "walled off" the bacteria and is protecting you from getting sick. Your doctor may recommend that you take medication to kill the bacteria so you will lower your risk of ever developing active TB disease. If your chest x-ray is abnormal and/or you have symptoms of TB disease your doctor will order additional tests to see if you have active disease.
What are the symptoms of TB disease?
Symptoms of TB disease can include any or all of the following:
- A cough lasting longer than 3 weeks
- Trouble breathing
- Pain in the chest
- Feeling tired all of the time
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Poor appetite
- Night sweats
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Coughing up blood
See your doctor if you have these symptoms.
What is directly observed therapy (DOT)?
To increase the success of TB disease treatment and decrease the risk of drug resistance, a health care worker observes each dose of TB medication taken.
Most persons believe they are able to take their medication without help. But 6 - 9 months is a long time to take antibiotics, especially after you start to feel better. Health care workers who provide DOT offer encouragement to complete treatment. People are human and humans are sometimes forgetful. DOT health care providers help people remember to take their medicine. They also check for harmful side effects and make sure the medicines are working as expected.
What is TB?
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium Tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). TB usually attack the lungs. Sometimes TB bacteria attack other parts of the body such as, the kidney, spine or brain. TB disease is a serious illness, but with proper treatment it can be cured.
Where can I learn more about TB?
The Northern Nevada Public Health's Tuberculosis Prevention and Control Program staff welcomes questions about tuberculosis. They can be reached at 775-785-4785.
There are many informative websites available:
Who is most likely to get TB?
Some people are more likely to be infected with the latent form of TB. These include:
- persons who were born in a foreign country with high rates of TB
- persons who have lived in a foreign country with high rates of TB
- persons who have spent time with someone with active TB disease
- persons who live or spend a lot of time in crowded places
Some people who are infected with latent TB have a greater risk of progressing to active TB disease. These include:
- persons who became infected with TB in the last 2 years
- children under 5 years of age
- new immigrants from countries with high rates of TB - persons who have been in the United States for less than 5 years
- persons with weakened immune systems
- persons with certain kinds of lung disease, such as silicosis
- persons with diabetes
- persons who have had stomach or bowel surgery
- persons who take certain medications for arthritis
- persons who take prednisone or other steroids for extended periods of time
- persons who have had cancer of the head, neck or leukemia
- persons with end stage renal disease
- persons who are extremely underweight (10% or more below ideal body weight)
- persons with an abnormal chest x-ray suggestive of old healed TB disease
- persons who had TB disease in the past but did not receive adequate treatment
- persons with HIV infection. Persons with HIV infection have the greatest risk of progressing to active TB disease.
Vasectomy
Can a vasectomy be reversed if I change my mind afterwards?
A vasectomy is a permanent operation. Some doctors try to undo a vasectomy with surgery, but it is expensive and many times does not work. Make sure that you do not want to father any more children before you have a vasectomy.
How do they do a vasectomy?
A vasectomy is done in a doctor’s office or clinic. The doctor numbs the area and then makes a small cut in the scrotum (skin around the testicles) to get to the tubes that carry the sperm (sperm ducts). The doctor then closes off the sperm ducts so that sperm cannot get into the semen (what comes out during an orgasm). When there are no sperm in the semen, you cannot cause a pregnancy.
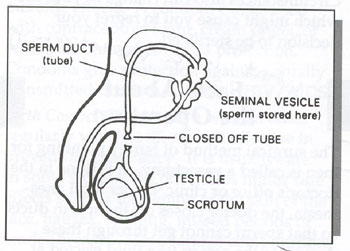
Are there other ways to prevent pregnancy besides a vasectomy?
Yes, there are several temporary ways to prevent pregnancy. A man can use a condom or a woman can use methods like birth control pills, the Depo shot, the patch, an IUD as well as others. If you would like more information about these and other temporary ways to prevent pregnancy, talk to your health care provider.
What are the benefits of a vasectomy?
With a vasectomy you don't have to worry about making a woman pregnant and you don't have to use a temporary method of family planning again (like birth control pills for women, condoms to prevent pregnancy, etc). However, the procedure will not protect you against STDs. A condom is still the best method for STD prevention.
What are the risks of a vasectomy?
Vasectomy is a safe and simple operation, but there is a small chance you could have problems afterwards. Some of the problems include:
- You may have temporary swelling around the area of the skin that was cut.
- You may have bruising that usually goes away on its own.
- You may get an infection on the skin or inside the scrotum.
- The operation may not make you sterile. A small number of men who have the operation will still be able to get a woman pregnant. The vasectomy is more than 99% effective.
What is a vasectomy?
A vasectomy is a sterilization operation for men. This means that after the operation a man cannot get a woman pregnant.</p.
Will I still be able to have sex after a vasectomy?
Yes. A vasectomy will not alter your sex drive. Your erections and orgasms will be the same. You will have the same amount of ejaculate (semen), but it will not contain sperm.
Waste Reduction, Recycling, and Disposal
Can I recycle yard clippings and other "green wastes"?
At this time, there is not a green waste program. However, you can build a compost pile from yard wastes that will provide nourishment and fertilizer for the garden and landscape.
For more information on how to construct a compost pile, consult your local nursery or the Master Gardener Program through the University of Nevada Cooperative Extension Office at 784-4848.
How do I get my recyclables picked up at the curbside in my neighborhood?
The residential recycling program in Reno, Sparks, and Washoe County is voluntary. You must contact Waste Management Inc., at 329-8822 to request recycling bins. They will be delivered to your home. Also, don’t forget to request a pickup schedule for recycled items. Your pickup day may be different that the regular garbage pickup.
How can I dispose of household products containing hazardous materials or chemicals?
The best way to prevent this disposal dilemma is to not purchase products that contain hazardous materials or chemicals. However, if you cannot share the product or donate it for use by others, please solidify the waste with kitty litter, dirt, or coffee grinds and throw it away.
How do I dispose of old computers?
If you are a homeowner, you should first try to donate the unit or turn it in to one of the used computer retailers in the area. The last and least attractive alternative is to dispose of it in the trash. If you are a business, your computers cannot be landfilled!
How do I get rid of old paint?
In Washoe County, there are several ways to dispose of household paint. First, remove the lids from the paint cans and let the contents dry to a solid form. If there is more than 1/2 inch of paint, add kitty litter to absorb it. When the material is solidified, you can dispose of it your household trash. Or, secondly, you may pour the paint directly on to plastic tarps being careful not to spill on to the ground; let it harden, and then roll up the tarps and place in your household trash.
Is there an option for single-stream recycling in Washoe County?
How can I start a waste reduction, recycling and a buy-recycled program in my work place?
Contact the Nevada Small Business Development Center's "Business Environmental Program" at 1-800-882-3233, or 689-6699, or contact EPA for the free "Business Guide for Reducing Solid Waste" at www.epa.gov.
Where can I dispose of used motor oil?
Most oil recycling centers will accept up to five gallons of used oil free-of-charge. Many of the large auto parts retailers in Washoe County will take motor oil from local residents. Make sure when transporting the oil, that it is in a secured container and is free of contamination by lubricants, gasoline, or antifreeze.
In other Northern Nevada Counties, call the State of Nevada Recycling Hotline at 1-800-597-5865.
Water Projects/Engineering
Can NNPH accept “red line” corrections on plans?
Can we meet with NNPH to discuss specific concerns or projects?
Meetings are held at the Northern Nevada Public Health (NNPH) office, and scheduling is completed through NNPH staff at 775-328-2434 or the ehsplanreview@nnph.org email.
What is required for a Final Map signature from NNPH?
What are the professional stamp and signature requirements for plan submittal?
Per the Nevada Board of Professional Engineer and Land Surveyors (NVBPELS), all plans are required to be stamped and signed in accordance with NAC 625.
Per the Nevada State Board of Architecture, Interior Design and Residential Design (NSBAIDRD), all plans are required to be stamped and signed in accordance with NAC 623.
How are separation distances determined?
All separations are determined from the outside pipe or enclosure. All plan submittals should be utilizing the outside diameter of pipe, catch basin, sewer main, storm drain, etc to identify the minimum separation distance allowed per NAC 445A.
Plans must demonstrate actual pipe diameters and ensure all separations meet the minimum requirements of NAC 445A.
How do I find the status of a construction plan review?
Email ehsplanreview@nnph.org
All plan review status, supplemental information for review, and other information regarding plans should be emailed to this location.
Emails should include the building permit number in the subject line.
What is the submittal process for a water project?
- All water projects are reviewed by Nevada Division of Environmental Protection (NDEP), Bureau of Safe Drinking Water (BSDW). You can find BSDW’s submittal requirements, fees, and other relevant information related to water projects at https://ndep.nv.gov/water/drinking-water/engineering-reviews.
- Northern Nevada Public Health serves as facility managers for groundwater and consecutive public water systems and should be the initial point of contact for all public water system general inquiries outside of water projects.
Last modified on 07/24/2025
Let’s Stay in Touch
Sign up for our newsletter
